How can NRI Students get MBBS Admission in India?
Medical colleges across India attract a large number of aspiring students each year. The National Medical Commission (NMC), formerly known as the Medical Council of India (MCI), oversees and regulates…
Medical colleges across India attract a large number of aspiring students each year. The National Medical Commission (NMC), formerly known as the Medical Council of India (MCI), oversees and regulates medical education in the country. Admission to India’s leading government and private medical institutions is primarily determined by performance in the NEET UG examination.
In addition to the 15% All India Quota and 85% State Quota, Deemed Universities and certain other institutions in India reserve 50% of their seats for NRI candidates, as per NMC guidelines. This quota is open to Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs), and Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs). However, qualifying for NEET-UG remains a mandatory requirement for all categories of applicants, including NRIs.
Many people assume that the NRI quota is available only in private medical colleges, but in reality, some state government colleges in India also offer seats under this category.
If you are an NRI seeking admission to an MBBS program in India, you might have several questions about eligibility, fees, and the admission process. This guide aims to clarify those concerns by providing detailed insights into which states offer NRI quota seats in both government and private colleges, along with information on fee structures. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how NRI admissions to Indian medical colleges work.
Who is Considered an NRI?
A student is categorized as a Non-Resident Indian (NRI) if they meet the following conditions:
- The individual is an Indian citizen or of Indian origin but currently resides outside India on a permanent or long-term basis.
- The person must have lived abroad for at least five consecutive years to qualify as an NRI.
- Generally, this means the candidate should have completed their 10th and 12th-grade education from a foreign country.
- Children of Indian citizens residing overseas for employment or business purposes are also recognized as NRIs.
- Students born abroad to parents of Indian origin are eligible to apply under the NRI category.
- Children of government employees (central or state) who are posted abroad on official duty or deputation are likewise considered NRIs.
MBBS Admission Eligibility for NRI Students
To secure admission to MBBS programs under the NRI quota, candidates must meet the following requirements:
- Possession of a valid passport is mandatory.
- Seats under the NRI quota are strictly reserved for genuine Non-Resident Indians.
- The candidate must have qualified in the NEET UG examination for the respective admission year.
- If applying under NRI sponsorship, the sponsor must be a close blood relative, such as a father, mother, brother, sister, uncle, or aunt.
- The candidate should have achieved at least 60% marks in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology in their Class 12 or equivalent examination.
- The applicant must be at least 17 years old and not more than 25 years old as of the year of NEET UG.
Benefits of MBBS Admission Through the NRI Quota
Let’s look into some of the benefits of getting MBBS admission through NRI quota:
1. Easier Access to Medical Seats
One of the major advantages of the NRI quota is the availability of specially reserved seats for Non-Resident Indian students. Since competition in the general category is intense and the cut-offs are extremely high, the NRI quota serves as a simplified and more attainable route to gain admission into top medical colleges in India.
2. Chance to Pursue Medical Education in India
Many Indian families living overseas prefer that their children study medicine in India because of the high academic standards, extensive clinical exposure, and cost-effective tuition compared to Western nations. The NRI quota enables these students of Indian origin to study in India without competing solely through the general category, maintaining their connection to the Indian education system.
3. Access to a Wide Selection of Colleges
A large number of private and deemed universities in India reserve seats for NRIs, providing a broad choice of reputable medical institutions across various states. This allows applicants to select colleges according to their preferences, financial considerations, and geographical convenience.
4. Global Career Opportunities
Completing an MBBS degree in India under the NRI quota gives students a strong clinical foundation and academic excellence recognized worldwide. Graduates often go on to qualify for international licensing exams such as USMLE, PLAB, or AMC, paving the way for successful global medical careers.
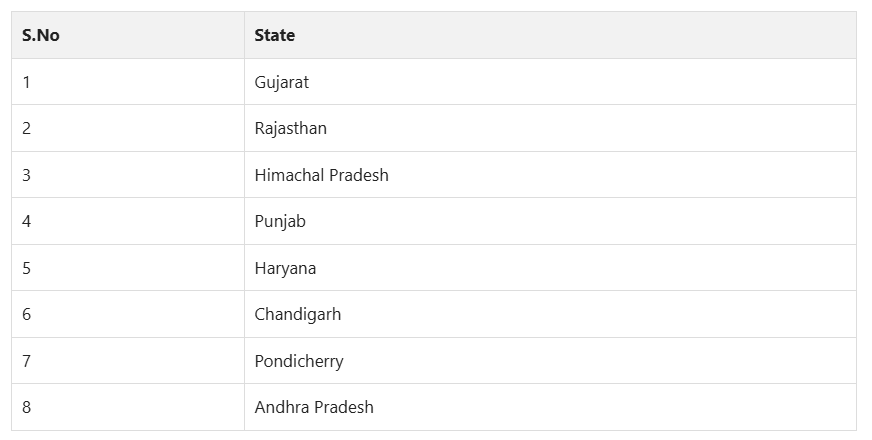
States Offering NRI Quota in Indian Government Medical Colleges
While the NRI quota is widely available in private and deemed universities, several Indian states also reserve a portion of seats for Non-Resident Indian (NRI) students in their government medical colleges. This quota enables students of Indian origin living abroad to pursue MBBS degrees in India’s top public medical institutions with world-class education and comparatively lower fees.
Below is a detailed list of states and union territories that provide NRI quota seats in government medical colleges, along with key details:
State Wise NRI Fees in Medical Colleges in India
The fee structure for NRI quota MBBS seats in India differs from state to state and depends on whether the college is government-run or private. Below is an overview of the approximate NRI fee structure in key states that offer NRI quota in government medical colleges:
- Himachal Pradesh:
The annual tuition fee for NRI students in government medical colleges is around USD 20,000 (or equivalent in INR) per year.
- Haryana:
In Haryana’s government medical institutions, the NRI fee for the MBBS course is approximately USD 25,000 at the time of admission, followed by USD 12,500 per year for the remaining four years of the program.
- Rajasthan:
As per the revised 2020 guidelines, NRI candidates are required to pay an initial deposit of USD 30,000 during admission, and a subsequent fee of USD 15,000 per semester thereafter.
- Puducherry (Pondicherry):
At Indira Gandhi Medical College and Research Institute, the total fee for NRI students is USD 100,000 for the complete course. This includes a refundable caution deposit of USD 15,000.
Additional Information
Apart from these states, all of them, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Puducherry, also extend NRI quota seats to private medical colleges, providing more options for eligible students.
Additionally, states such as Gujarat, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, Kerala, Karnataka, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu offer NRI quota seats only in self-financed private medical institutions and not in government colleges.
Moreover, all Deemed Medical Universities across India reserve 15% of their total MBBS seats for NRI students, with counseling and seat allocation conducted through the Medical Counselling Committee (MCC).
Final Words
If you’re an NRI aspiring to pursue MBBS admission in India, Olympia Education is here to guide you every step of the way. From application assistance and counselling support to seat allocation under the NRI quota, our expert team ensures a smooth and successful admission process into top medical colleges.
Contact Us

Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the NRI quota in MBBS admissions?
The NRI quota is a special category of seats reserved in medical colleges across India for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs), Overseas Citizens of India (OCIs), and Persons of Indian Origin (PIOs). It allows students of Indian origin living abroad to secure admission in MBBS programs in both government and private medical colleges without competing entirely in the general category.
2. Who is eligible to apply under the NRI quota?
To qualify for the NRI quota, a student must be either an NRI, OCI, or PIO, or be sponsored by a close blood relative who is an NRI (such as a parent, sibling, uncle, or aunt). The candidate must have passed Class 12 (or equivalent) with Physics, Chemistry, and Biology as main subjects and scored at least 60% marks. Additionally, qualifying the NEET UG exam is mandatory.
3. Is NEET UG compulsory for NRI students?
Yes. NEET UG is compulsory for all NRI candidates seeking MBBS admission in India, regardless of whether the seat is under the NRI quota or the general category. Without a valid NEET score, no student, Indian or NRI, can be admitted to a medical college in India.
4. Do government medical colleges offer NRI quota seats?
Yes, several states in India have reserved NRI seats in government medical colleges. These include Gujarat, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Chandigarh, Puducherry, and Andhra Pradesh. The number of NRI seats and the fee structure vary by state and institution.
5. What is the fee structure for MBBS admission under the NRI quota?
The fees under the NRI quota are higher than those for Indian residents but vary depending on the college and state. On average, the tuition fees range between USD 20,000 and USD 50,000 per year in government institutions, while private and deemed universities may charge more. Some states also require a one-time deposit at the time of admission.
6. How can NRI students apply for MBBS admission in India?
NRI students must first register and appear for NEET-UG, conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA). After qualifying, they can participate in state or central counseling depending on the college type:
- MCC (Medical Counselling Committee) conducts counseling for Deemed and Central Universities, and
- State counseling authorities handle admissions for state government and private medical colleges offering NRI quota seats.





